11229 Brooklyn Pediatric Dentistry
Pediatric Dentistry in Brooklyn 11229
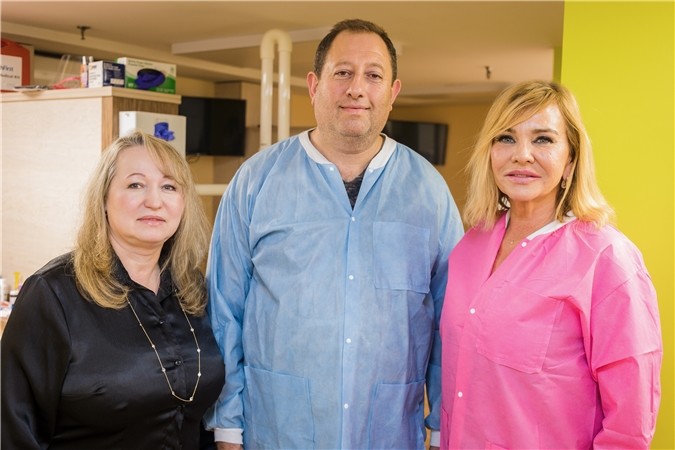
Brooklyn Pediatric Dentist – Dr. Natalia Blazhkevich
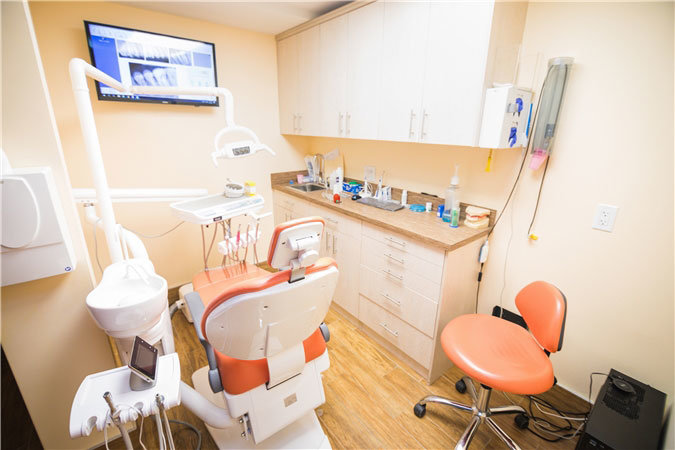
Our Brooklyn pediatrics team, and our pediatric dentist
Our office implements the following services:
- Proper brushing and flossing
- Custom fluoride therapy
- Decay - preventing sealents
- Nutritional counseling
- Play based desensitization
- Behavioral modification
- Positive reinforcement
- In - office sedation
The number one objective of Dr. Natalia Blazhkevich
Our Brooklyn pediatric team is to help your child maintain a healthy, happy and attractive smile that lasts a lifetime.
Services

Have a question that is not answered below? Feel free to give us a call and ask!
Frequently Asked Questions about a Pediatric Dentist
Primary teeth, or baby teeth are important for:
- proper chewing and eating
- providing space for the permanent teeth and guiding them into the correct position
- permitting normal development of the jaw bones and muscles.
Tooth brushing is one of the most important tasks for good oral health. Many toothpastes, and/or tooth polishes, however, can damage young smiles. They contain harsh abrasives, which can wear away young tooth enamel. When looking for a toothpaste for your child, make sure to pick one that is recommended by the American Dental Association as shown on the box and tube. These toothpastes have undergone testing to insure they are safe to use.
Remember, children should spit out toothpaste after brushing to avoid getting too much fluoride. If too much fluoride is ingested, a condition known as fluorosis can occur.
A few suggestions to help your child get through thumb sucking:
- Children often suck their thumbs when feeling insecure. Focus on correcting the cause of anxiety, instead of the thumb sucking.
- Children who are sucking for comfort will feel less of a need when their parents provide comfort.
- Reward children when they refrain from sucking during difficult periods, such as when being separated from their parents.
- Our pediatric dentist can encourage children to stop sucking and explain what could happen if they continue.
- If these approaches don’t work, remind the children of their habit by bandaging the thumb or putting a sock on the hand at night. Our Midtown pediatric dentist may recommend the use of a mouth appliance.
Developing malocclusions, or bad bites, can be recognized as early as 2-3 years of age. Often, early steps can be taken to reduce the need for major orthodontic treatment at a later age.
Stage I – Early Treatment: This period of treatment encompasses ages 2 to 6 years. At this young age, the kids dentist is concerned with underdeveloped dental arches, the premature loss of primary teeth, and harmful habits such as finger or thumb sucking. Treatment initiated in this stage of development is often very successful and many times, though not always, can eliminate the need for future orthodontic/orthopedic treatment.
Stage II – Mixed Dentition: This period covers the ages of 6 to 12 years, with the eruption of the permanent incisor (front) teeth and 6 year molars. Treatment concerns deal with jaw malrelationships and dental realignment problems. This is an excellent stage to start treatment, when indicated, as your child’s hard and soft tissues are usually very responsive to orthodontic or orthopedic forces.
Stage III – Adolescent Dentition: This stage deals with the permanent teeth and the development of the final bite relationship.
Process by which an infants first teeth (often called “baby teeth” or “milk teeth”) appear by emerging through the gums, typically arriving in pairs. Teething may start as early as three months or as late as twelve months. The first teeth typically appear between six and eight months.
Teething may cause a slightly elevated temperature, but not rising into the febrile range, 100–101 °F (37.8–38.3 °C).
The level of pain that a baby can handle will be different for each child. Some may be a lot fussier than others while they are teething. The soreness and swelling of the gums before a tooth comes through is the cause for the pain and fussiness a baby experiences during this change. These symptoms usually begin about three to five days before the tooth shows, and they disappear as soon as the tooth breaks the skin. Some babies are not even bothered by teething.
Common symptoms include drooling/dribbling, mood changes, irritability or crankiness, and swollen gums. Crying, sleeplessness, restless sleep at night, and mild fever are also associated with teething. Teething can begin as early as 3 months and continue until a child’s third birthday. In rare cases, an area can be filled with fluid and appears over where a tooth is erupting and cause the gums to be even more sensitive. Pain is often associated more with large molars since they cannot penetrate through the gums as easily as the other teeth.
Some noticeable symptoms that a baby has entered the teething stage include chewing on their fingers or toys to help relieve pressure on their gums. Babies might also refuse to eat or drink due to the pain. Symptoms will generally fade on their own, but a doctor should be notified if they worsen or are persistent. Teething may cause signs and symptoms in the mouth and gums, but it doesn’t cause problems elsewhere in the body.
Pulling on the ears is another sign of pain; the pain in the mouth throbs throughout the baby’s head so they pull their ears believing that it will provide relief. Mild rash can develop around the mouth due to skin irritation that is caused by excessive drooling or dribbling. If you see this type of behavior contact Brooklyn pediatric dentist.
One serious form of decay among young children is baby bottle tooth decay. This condition is caused by frequent and long exposures of an infant’s teeth to liquids that contain sugar. Among these liquids are milk (including breast milk), formula, fruit juice and other sweetened drinks.
Putting a baby to bed for a nap or at night with a bottle filled with a liquid other than water can cause serious and rapid tooth decay. Sweet liquid pools around the child’s teeth giving plaque bacteria an opportunity to produce acids that attack tooth enamel. If you must give the baby a bottle as a comforter at bedtime, it should contain only water. If your child won’t fall asleep without the bottle and its usual beverage, gradually dilute the bottle’s contents with water over a period of two to three weeks.
After each feeding, wipe the baby’s gums and teeth with a damp washcloth or gauze pad to remove plaque. The easiest way to do this is to sit down, place the child’s head in your lap or lay the child on a dressing table or the floor. Whatever position you use, be sure you can see into the child’s mouth easily.
Chronic, long-term mouth odor can be a sign of more serious illness. See your dentist if this is a concern.
Brooklyn pediatric dentist has a lot to say about piercings.
You might not be surprised anymore to see people with pierced tongues, lips or cheeks, but you might be surprised to know just how dangerous these piercings can be. There are many risks involved with oral piercings, including chipped or cracked teeth, blood clots, blood poisoning, heart infections, brain abscess, nerve disorders (trigeminal neuralgia), receding gums or scar tissue. Your mouth contains millions of bacteria, and infection is a common complication of oral piercing. Your tongue could swell large enough to close off your airway!
Common symptoms after piercing include pain, swelling, infection, an increased flow of saliva and injuries to gum tissue. Difficult-to-control bleeding or nerve damage can result if a blood vessel or nerve bundle is in the path of the needle.
So follow the advice of the American Dental Association and give your mouth a break – skip the mouth jewelry.
- A sore that won’t heal.
- White or red leathery patches on the lips, and on or under the tongue.
- Pain, tenderness or numbness anywhere in the mouth or lips.
- Difficulty chewing, swallowing, speaking or moving the jaw or tongue; or a change in the way the teeth fit together.
